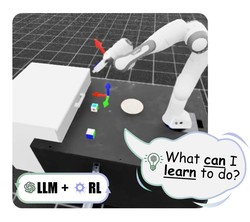
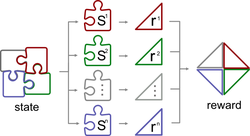
Agentic Skill Discovery
We propose an LLM-driven framework that enables robots to autonomously discover useful skills from scratch. By generating tasks, …
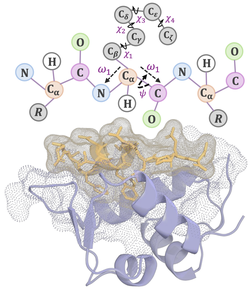
Joint Design of Protein Surface and Backbone Using a Diffusion Bridge Model
PepBridge jointly designs receptor-complementary protein surfaces and full 3D structures from a receptor’s point-cloud surface. It uses …
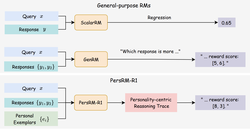
PersRM-R1: Enhance Personalized Reward Modeling with Reinforcement Learning
We propose PersRM-R1, a reasoning-based reward model that learns personal preferences from just a few examples. Using synthetic data …
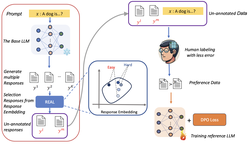
REAL: Response Embedding-Based Alignment for LLMs
We propose REAL (Response Embedding-based Alignment for LLMs), a method to improve alignment efficiency by selecting less ambiguous, …
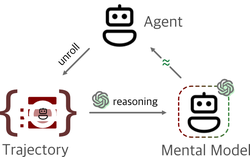
Mental Modeling of Reinforcement Learning Agents by Language Models
This study explores whether LLMs can mentally model decision-making agents by reasoning over their behavior and state transitions from …
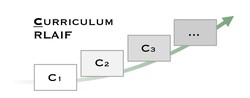
Curriculum-RLAIF: Curriculum Alignment with Reinforcement Learning from AI Feedback
We propose Curriculum-RLAIF, a data-centric framework that improves reward model generalizability by training on preference pairs of …
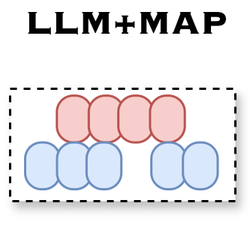
LLM+MAP: Bimanual Robot Task Planning Using Large Language Models and Planning Domain Definition Language
LLM+MAP is a bimanual planning framework that combines GPT-4o with multi-agent task planning to enable efficient and logically …
Enhancing Zero-Shot Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Large Language Models through Logic
We propose LoT (Logical Thoughts), a framework that improves large language models’ reasoning at inference time by applying symbolic …
Large Language Models for Orchestrating Bimanual Robots
LABOR uses LLMs to orchestrate control policies for long-horizon bimanual manipulation tasks. By leveraging task reasoning and …
Details Make a Difference: Object State-Sensitive Neurorobotic Task Planning
We introduce OSSA (Object State-Sensitive Agent), a task-planning agent using pre-trained LLMs and VLMs to generate plans sensitive to …
Causal State Distillation for Explainable Reinforcement Learning
We propose reward decomposition methods for better decision-making explainality.
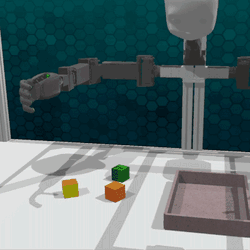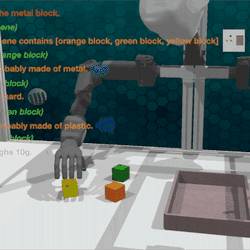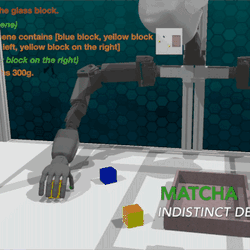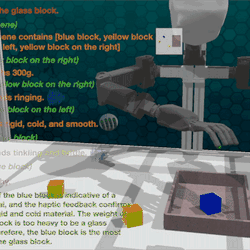
Chat with the Environment: Interactive Multimodal Perception Using Large Language Models
We present Matcha agent, an interactive perception framework that uses LLMs to guide robots in gathering multimodal sensory data …
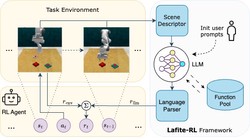
Accelerating Reinforcement Learning of Robotic Manipulations via Feedback from Large Language Models
Lafite-RL is a framework that leverages Large Language Models to provide natural language feedback for guiding reinforcement learning …
Internally Rewarded Reinforcement Learning
We introduce Internally Rewarded Reinforcement Learning (IRRL), where rewards are generated by a jointly learned internal model rather …
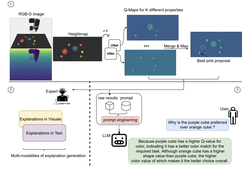
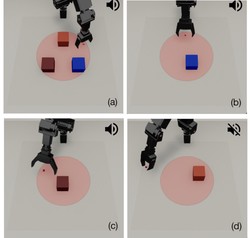
A Closer Look at Reward Decomposition for High-Level Robotic Explanations
Explainable Q-Map improves the transparency of RL agents by combining reward decomposition with abstract action spaces, enabling clear, …
Impact Makes a Sound and Sound Makes an Impact: Sound Guides Representations and Explorations
We propose the Intrinsic Sound Curiosity Module (ISCM) to use sound as an informative modality for unsupervised reinforcement learning. …
Density Weighted Diversity based Query Strategy for Active Learning
DWDS is a density-weighted diversity strategy for active learning in deep learning. It selects informative and representative samples …